Extrasolar system small bodies
My research includes:
Asteorid tidal disruption as a possible origin of Sgr A* flares (Zhou et al., 2026b)
Sgr A*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way, frequently produces short-lived flares with luminosities above 10^34 erg/s across multiple wavelengths, yet their physical origin remains uncertain. This study revisits the idea that small planetary bodies from the stellar disk, along with fragments created by their tidal disruption, could be responsible for this activity. Building on earlier work, the analysis improves the modeling by including limits set by material strength on when tidal disruption occurs, and by examining how the resulting fragments evaporate.
The study investigates both tidal and gas-driven fragmentation for small bodies with either rubble-pile or monolithic structures, using constraints from missions such as NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and JAXA’s Hayabusa2 to estimate fragment survival under aerodynamic heating. The resulting emission is modeled as meteor-like fireball flares produced by ablation. The results show that planetary fragments can survive down to about 8 R•, matching flare locations inferred from observations, and can generate luminosities of 10^34–10³⁶ erg s⁻¹ when the parent bodies are a few kilometers across. The predicted flare frequency–luminosity distribution follows a power law with index 1.83, consistent with observed values of 1.65–1.9, while the flare duration scales as t_f ∝ L^−1/3, also in line with observations. Assuming the young stars around Sgr A★ host a reservoir of small bodies comparable in mass to the primordial Kuiper belt, together with close-in super-Earths and long-period Neptunes, the authors conclude that the tidal disruption and thermal evaporation of such bodies provide a plausible explanation for the observed flares.
White dwarf pollution (Zhou et al. 2024b)
- Evolution of volatile content in icy objects
White dwarfs are found to be contaminated by heavy elements, which are believed to originate from external sources such as planetary materials. However, most of polluted white dwarfs are found to be polluted by refractory materials, which is not consistent with the compositions of icy objects in the outer solar system.
We proposed that the volatile gas in the disk could be shielded by the magnetic field. In the process of orbital circularization, volatile content release from the surface and gas atoms are photoionized on a short timescale. The charged particles interact with the white dwarf magnetic field and are shielded from the corotation radius, where the spin period of white dwarf equals the Keplerian period.
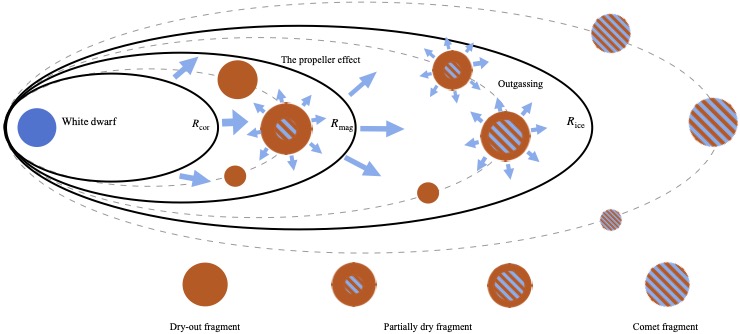
- White dwarf pollution detection using machine learning based tools (in progress)
Interstellar objects (Zhou 2020; Zhou et al. 2022)
- Rotational evolution of interstellar objects in the interstellar space (Zhou 2020)
`Omuamua was found to be in a non-principal-axis rotation state, namely tumbling. I proposed that the interaction with interstellar medium (gas or/and dust) could produce a torque triggering the tumbling motion. The timescale is a few Gyrs for Oumuamua-sized objects and is linear to the square of the size.
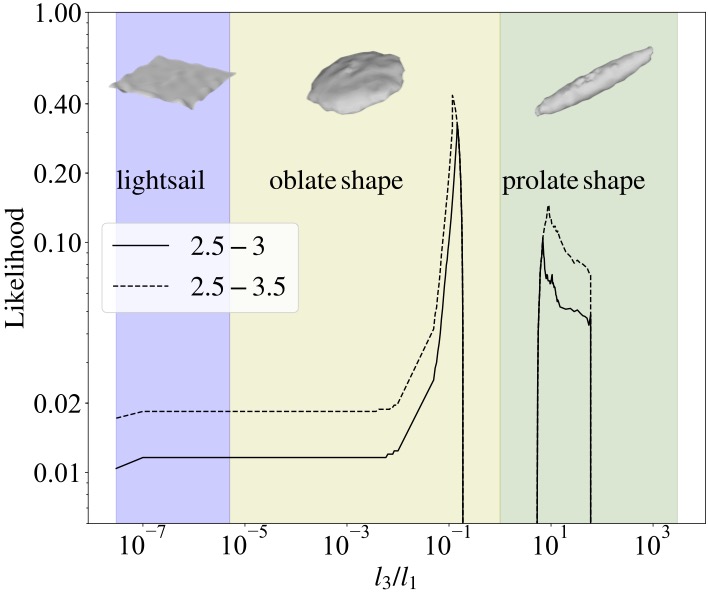
- Constraints on `Oumuamua’s shape (Zhou et al. 2022)
By analyzing the observation data of `Oumuamua, we found the most probable shape is oblate shape. We found the hypothesis of Oumuamua as a lightsail is not favored by the observed light curve and the dynamics in the interstellar space.
Debris disk
- Orbital evolution during RGB and AGB phase (in progress)
The debris disk expands during the red giant branch (RGB) and asymptotic giant branch (AGB) phase. The surviving objects lead to pollution in white dwarfs, providing valuable information on compositions and architectures of exo-planetary system. We model the orbital evolution of asteroids in during the RGB and AGB phase, which will tell us the composition and distribution of the progenitors of debris disks around the white dwarf.
- Spectra analysis of debris disks (in progress)